Chapter2: Network Layer (Part3)
7. NAT
In a system where IP addresses are private, each host must have a unique IP address; private hosts who do not want to connect to the Internet can use any private IP address as long as it is not assigned to another machine on the same private network. This allows greater flexibility for network design and easier growth.
We have three private address ranges :

All these addresses are not routed in the Internet network. Routers are all configured to eliminate private addresses, which are not routable on the internet network.
In a private intranet, we use private addresses. When hosts of this private intranet want to connect to the Internet, private addresses are translated into public addresses. This translation is called NAT (Network Address Translation). The network device who performs this translation is the router (WAN edge router). Network Address Translation (NAT) is a service that enables private IP networks to use the internet and cloud. NAT translates private IP addresses in an internal network to a public IP address before packets are sent to an external network.
Public IP addresses are used by hosts that need to be accessible from the internet. Each public address must be unique on the internet in order to be stable. It is the IANA organization which is responsible for ensuring that there is no duplicate. To obtain a public IP address, you must contact an ISP (Internet Service Provider).
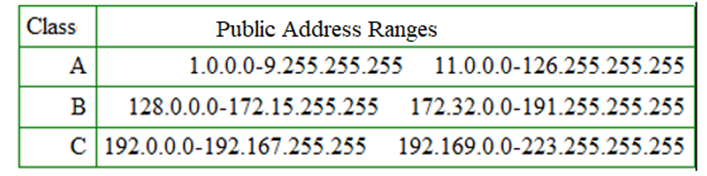
In the following, the three public address ranges :
Two companies can have the same private addresses. To communicate with each other and avoid any conflict or to connect to the internet the NAT is used. Therefore, NAT is not just for surfing the Internet.
There are four types of important addresses in NAT: [ref1]
· Inside local address—The IP address assigned to a host on the inside network. This is the address configured as a parameter of the computer OS or received via dynamic address allocation protocols such as DHCP. The address is likely not a legitimate IP address assigned by the Network Information Center (NIC) or service provider.
· Inside global address—A legitimate IP address assigned by the NIC or service provider that represents one or more inside local IP addresses to the outside world.
· Outside local address—The IP address of an outside host as it appears to the inside network. Not necessarily a legitimate address, it is allocated from an address space routable on the inside.
· Outside global address—The IP address assigned to a host on the outside network by the host owner. The address is allocated from a globally routable address or network space.
Packets sourced on the inside portion of the network have an inside local address as the source address and an outside local address as the destination address of the packet, while the packet resides on the inside portion of the network. When that same packet gets switched to the outside network, the source of the packet is now known as the inside global address and the destination of the packet is known as the outside global address.
Conversely, when a packet is sourced on the outside portion of the network, while it is on the outside network, its source address is known as the outside global address. The destination of the packet is known as the inside global address. When the same packet gets switched to the inside network, the source address is known as the outside local address and the destination of the packet is known as the inside local address. We have three kinds of NAT :
Static NAT
In this kind of NAT, we map a local IP address to a public IP address (permanent mapping from a private address to a public address). It is particularly useful when a device needs to be accessible from the outside. Web server for example. This image provides an example.

Figure 2.2- Example of NAT.
Dynamic NAT
Multiple local IP addresses correspond to multiple public IP addresses that come from an IP pool. This type of
NAT is very useful when two companies that use the same private addressing plan merge.
PAT (Port address translation) or NAT Overload
Maps multiple private addresses to a single public address. Port numbers will be randomly assigned to help track the connection. The most common use of PAT is in the home in the Internet modem/router.
