Psycholinguistics CM
مخطط أسبوعي
-
-
Lectures of this module emphasize the act or the process of acquiring a language in addition to all the stages of CLA and the major theories which have dealt with Child Language Acquisition.
-
-
-
To develop understanding of the relationship between language and the processes of the brain and mind.
- Presenting schools of thought, concepts, theories,and a number of approaches related to psycholinguistics.
- Help the learners to undersatand the role of the brain in processing language.
-
Reinforcing teacher's out put and clarifying student's ambiguities
-
The module of psycholinguistics requires the teacher as a guider and student's to be self -directed.
-
This activity's main aim was to shore up what was discussed during the lecture. Students have tested themselves first then we moved to discussion.
-
-
-
Psycholinguistics as any other discipline has taken many forms of inquiry i.e.
Diary Studies: (from 1877-1930)
- Language development was studied through diary studies by recording child speech.
*Language Sample Studies: (from 1930-1957)
- Instead of collecting data of a single child they collect data from a large number of children at a certain stage.
*Linguistic Studies: (from 1957 onwards)
Instead of focusing just at the utterance of a child, they tried to understand the rules behind it.
-
-
-
Developmental psycholinguistics/ Child language acquisition is one of the paramount concern of psycholinguistics.- It provides us with all what is related to how does a child capture and deals with his/her first language? starting from the smallest details that take place during the first weeks of his life the to the multiple words stage .
-
This video will provide you with further information concerning language and language varieties acquisition.
-
-
-
No Langauge but a cry!
Tennyson quoted in Scovel 1998) contended that “our first efforts at speech are not words but cries”
So runs my dreams, but what am I?
An infant crying in the night
An infant crying for the light
-
-
-
The first sounds that infants are able to produce are soft vowels

At the stage of babbling, babies start to make one- syllable sounds.

-
-
-
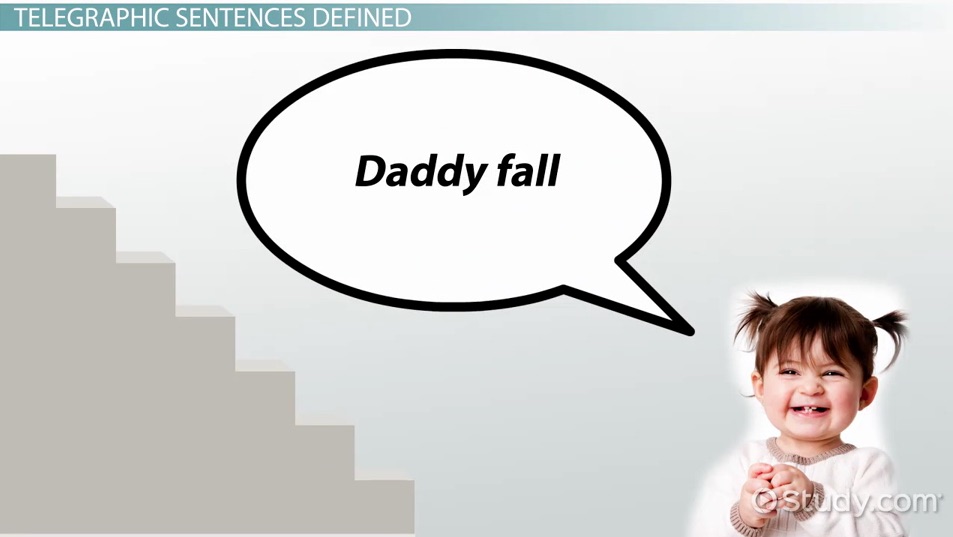
In this stage, children begin stringing more than two words together, perhaps three or four or five at a time. However, the style of speaking children use in this stage resembles the way of writing that used to be used in telegrams. That’s why this stage is called telegraphic.
-
-
-
Chomsky believes that every child has a ‘language acquisition device’ or LAD which encodes the major principles of a language and its grammatical structures into the child’s brain. Children have then only to learn new vocabulary and apply the syntactic structures from the LAD to form sentences. Chomsky points out that a child could not possibly learn a language through imitation alone because the language spoken around them is highly irregular – adult’s speech is often broken up and even sometimes ungrammatical.
-
-
